Mysql If Exists Update Else Insert Query In Oracle
Feb 17, 2008 SQL: If Exists Update Else Insert. (it’s a quick port to MySQL and Oracle. Generate the 'If Exist Update Else Insert' statement for all records of.
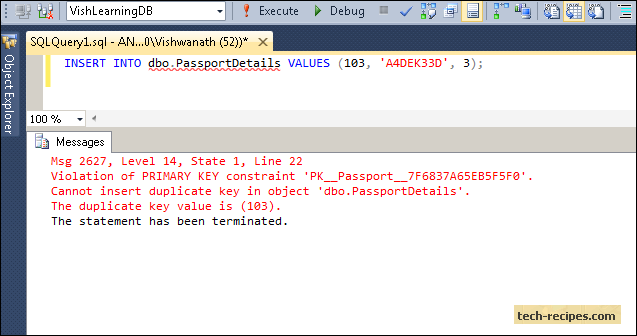
You can try to use' INSERT. ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE' syntax If you specify ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE, and a row is inserted that would cause a duplicate value in a UNIQUE index or PRIMARY KEY, an UPDATE of the old row is performed. For example, if column a is declared as UNIQUE and contains the value 1, the following two statements have identical effect: INSERT INTO table (a,b,c) VALUES (1,2,3) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE c=c+1; UPDATE table SET c=c+1 WHERE a=1; The ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE clause can contain multiple column assignments, separated by commas.
Jjos2xl Keygen.. With ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE, the affected-rows value per row is 1 if the row is inserted as a new row and 2 if an existing row is updated. If column b is also unique, the INSERT is equivalent to this UPDATE statement instead: UPDATE table SET c=c+1 WHERE a=1 OR b=2 LIMIT 1; If a=1 OR b=2 matches several rows, only one row is updated. In general, you should try to avoid using an ON DUPLICATE KEY clause on tables with multiple unique indexes.
You can use the VALUES(col_name) function in the UPDATE clause to refer to column values from the INSERT portion of the INSERT. Deadly Boss Mods 3.3 Patch. UPDATE statement. In other words, VALUES(col_name) in the UPDATE clause refers to the value of col_name that would be inserted, had no duplicate-key conflict occurred. This function is especially useful in multiple-row inserts. The VALUES() function is meaningful only in INSERT. UPDATE statements and returns NULL otherwise.
Example: INSERT INTO table (a,b,c) VALUES (1,2,3),(4,5,6) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE c=VALUES(a)+VALUES(b); That statement is identical to the following two statements: INSERT INTO table (a,b,c) VALUES (1,2,3) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE c=3; INSERT INTO table (a,b,c) VALUES (4,5,6) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE c=9; If a table contains an AUTO_INCREMENT column and INSERT. UPDATE inserts a row, the LAST_INSERT_ID() function returns the AUTO_INCREMENT value. If the statement updates a row instead, LAST_INSERT_ID() is not meaningful. However, you can work around this by using LAST_INSERT_ID(expr). Suppose that id is the AUTO_INCREMENT column.
To make LAST_INSERT_ID() meaningful for updates, insert rows as follows: INSERT INTO table (a,b,c) VALUES (1,2,3) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE id=LAST_INSERT_ID(id), c=3; The DELAYED option is ignored when you use ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE.
13.2.10.6 Subqueries with EXISTS or NOT EXISTS If a subquery returns any rows at all, EXISTS subquery is TRUE, and NOT EXISTS subquery is FALSE. For example: SELECT column1 FROM t1 WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM t2); Traditionally, an EXISTS subquery starts with SELECT *, but it could begin with SELECT 5 or SELECT column1 or anything at all. MySQL ignores the list in such a subquery, so it makes no difference.
For the preceding example, if t2 contains any rows, even rows with nothing but NULL values, the EXISTS condition is TRUE. This is actually an unlikely example because a [NOT] EXISTS subquery almost always contains correlations. Here are some more realistic examples.
• What kind of store is present in one or more cities? SELECT DISTINCT store_type FROM stores WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM cities_stores WHERE cities_stores.store_type = stores.store_type); • What kind of store is present in no cities? SELECT DISTINCT store_type FROM stores WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM cities_stores WHERE cities_stores.store_type = stores.store_type); • What kind of store is present in all cities? SELECT DISTINCT store_type FROM stores s1 WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT * FROM cities WHERE NOT EXISTS ( SELECT * FROM cities_stores WHERE cities_stores.city = cities.city AND cities_stores.store_type = stores.store_type)); The last example is a double-nested NOT EXISTS query. That is, it has a NOT EXISTS clause within a NOT EXISTS clause.